In this JavaScript Array article, we will focus on the array methods used to define a list of items.
JavaScript Array
An array is a data structure that contains a list of elements that store multiple values under a single variable.
To declare an array in JavaScript use any keyword with square brackets [ ] and enclose all the elements within them. The syntax is as follows:
let ListItems = ["shoes", "watch", "bag"];
Array Index value
- The index value of an array indicates the position of the element within the array (starting from 0). You will understand better from this image below:
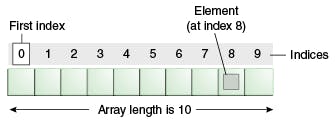
Modifying an array
- Array elements are modified using the
index valuesof the elements.
Example
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8];
number[0]="empty";
number[2]
output:
['empty', 2, 'empty', 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
Length property of an array
- Length of an array can be found using the length property.
Example
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8];
console.log(numbers.length)
output:
8
JavaScript Array Methods
- There are different JavaScript array methods in order to perform various tasks such as:
1. push()
- It is used to add a new element at the end of an array.
Example
let listItems = ["bag", "shoes", "dress"];
listItems.push("watch");
console.log(listItems);
Output:
['bag', 'shoes', 'dress','watch']
2. pop()
- It is exactly opposite of the
push()method. Yes, you have guessed it right. It is used to remove the last element of an array.
Example
let listItems = ["bag", "shoes", "dress"];
listItems.pop();
console.log(listItems);
Output:
['bag', 'shoes']
3. shift()
- Shifting is similar to popping, working on the first element instead of the last. The
shift()method removes the first array element and shifts all other elements to a lower index. It will return to you the string that has been shifted out.
Example
let listItems = ["bag", "shoes", "dress"];
listItems.shift();
console.log(listItems);
Output:
['shoes', 'dress']
4. unshift()
- The
unshift()method adds a new element at the beginning of an array and unshifts older elements. It is similar toPush().
Example
let listItems = ["bag", "shoes", "dress"];
listItems.unshift("watch");
console.log(listItems);
Output:
['watch','bag', 'shoes', 'dress']
5. concat()
- The
concat()method creates a new array by concatenating or merging existing arrays. It does not modify the existing array and always returns a new array.
Example
let arr1 = ["red", "blue", "green"];
let arr2 = ["colors", "spraypaint", "brush"];
let newArr = arr1.concat(arr2);
console.log(newArr);
Output:
[ 'red', 'blue', 'green', 'colors', 'spraypaint', 'brush' ]
6. toString()
- The
toString()method is used to convert an array to a string of array values, separated by commas.
Example
let colors = ["red", "blue", "green"];
console.log(colors.toString());
Output:
red,blue,green
7. join()
The
join()method works same astoString(). It is used to join all array elements into a string, but in addition, you can specify the separator.Example
let colors = ["red", "blue", "green"];
console.log(colors.join("+"));
Output:
red+blue+green
8. sort()
- It is used to arrange an array alphabetically in ascending order.
Example
let names = ["Yasir", "Shariq", "Afzal", "Zaiem", "Rehan"];
console.log(names.sort());
Output:
[ 'Afzal', 'Rehan', 'Shariq', 'Yasir', 'Zaiem' ]
9. slice()
- To explain
slice(), let us take an example: Suppose there is a cake in front of you and you want a slice of it, so you cut the cake and remove a slice from it. The use ofslice()is also the same.
- So, the
slice()method is used to slice out a piece of an array into a new array. It creates a new array without removing any elements from the source array. It will return the value that has been sliced out from the array.
Example
let colors = ["red", "blue", "green", "yellow", "orange"];
console.log(colors.slice(1, 3));
Output:
[ 'blue', 'green' ]
10. splice()
splice()is like cutting a piece of cake and replacing that piece with a new piece of cake.
- So, the
splice()method is used to replace a piece of an array and form a new array.
Syntax
splice(start);
splice(start, deleteCount);
splice(start, deleteCount, item1);
splice(start, deleteCount, item1, item2, itemN);
Example
const months = ["Jan", "March", "April", "June"];
months.splice(1, 0, "Feb");
// inserts at index 1
console.log(months);
// expected output: Array ["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April", "June"]
months.splice(4, 1, "May");
// replaces 1 element at index 4
console.log(months);
// expected output: Array ["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April", "May"]
Output:
["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April", "June"]
["Jan", "Feb", "March", "April", "May"]
11. includes()
- The includes() method determines whether an array includes a certain value among its entries, returning true or false as appropriate.
Example
let array1 = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(array1.includes(2));
output
true
12. fill()
- The
fill()method changes all elements in an array to a given value, from a start index (default 0) to an end index (default array.length). It returns the modified array.
Syntax
fill(value)
fill(value, start)
fill(value, start, end)
Example
let x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
console.log(x.fill('h', 1, 3));
output
[ 1, 'h', 'h', 4, 5, 6 ]
13. filter()
- The filter() method creates a shallow copy of a portion of a given array, filtered down to just the elements from the given array that pass the test implemented by the provided function.
Syntax
filter((element) => { /* … */ } )
Example
var a = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
var final_a = a.filter((num) => num != 5);
console.log(final_a);
output
[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9 ]
So, this was it for the methods of the javascript array. You will be more confident about the concept of javascript arrays only after some practice, so get started with the practicing part.
If you liked my article, then don't forget to drop a like, and please give your feedback in the comment section.